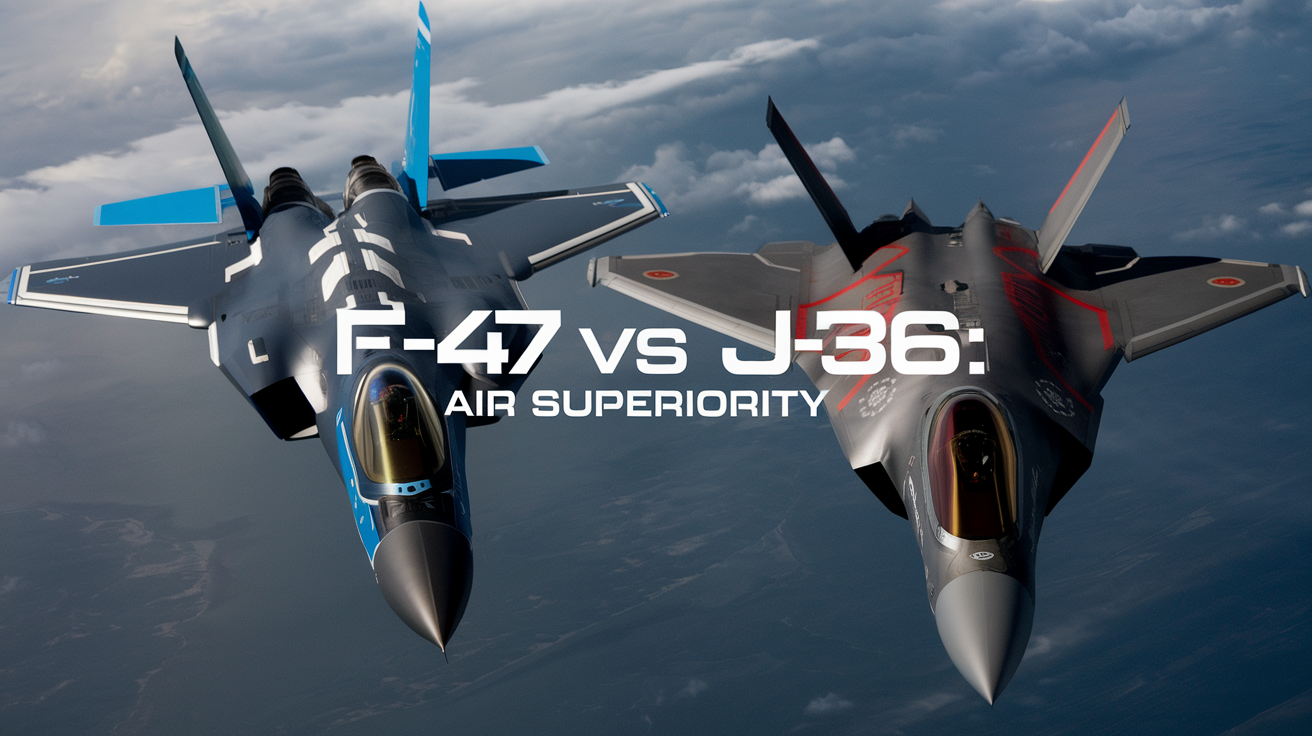
In the high-stakes world of aerial combat, two titans are poised to clash in the skies: the American F-47 and China’s J-36. These next-generation fighter jets represent the pinnacle of military aviation technology, each vying for supremacy in the ever-evolving landscape of air warfare. 🛩️💨
As nations race to develop sixth-generation aircraft, the F-47 and J-36 stand out as formidable contenders, embodying their respective countries’ strategic ambitions and technological prowess. The F-47, part of America’s Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program, promises enhanced stealth, AI integration, and drone collaboration. Meanwhile, the J-36 boasts a unique trio-engine layout and focuses on long-range strike capabilities. But which of these cutting-edge machines truly reigns supreme? 🤔
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the specs, capabilities, and strategic implications of these advanced fighter jets. From comparing their stealth technologies to analyzing their potential impact on global military dynamics, we’ll explore how the F-47 and J-36 are set to reshape the future of aerial warfare. Buckle up as we embark on a thrilling journey through the world of next-gen air dominance! ✈️🚀
F-47: America’s Next-Gen Air Dominance

Design features and capabilities
The F-47, America’s sixth-generation fighter, boasts advanced stealth technology, enhanced range, and lower operational costs compared to its predecessors. With speeds around Mach 2, it offers superior air dominance capabilities. The aircraft’s design incorporates innovative elements like a canard configuration, reflecting a shift towards more sophisticated air combat strategies.
Development timeline and Boeing’s contract
| Milestone | Details |
|---|---|
| 2020 | Initial experimental tests begin |
| March 2025 | Boeing awarded EMD contract |
| End of decade | Expected operational debut |
Integration with drone technology and AI
The F-47 is designed to integrate with drone swarms and Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA), forming a “family of systems” approach. This integration enhances adaptability and reduces manpower requirements, revolutionizing air combat capability for future conflicts.
With the F-47’s capabilities outlined, let’s now explore China’s advanced fighter jet, the J-36, to understand how it compares in the realm of next-generation air dominance.
J-36: China’s Advanced Fighter Jet

A. Unique design elements and propulsion system
The Chengdu J-36, China’s advanced fighter jet, features a tailless diamond-shaped double-delta wing design optimized for stealth and high-speed performance. Its unique configuration includes a streamlined cockpit canopy, split ruddervons, and extensive internal weapon bays. The J-36 utilizes a trijet propulsion system, potentially addressing China’s historical challenges in producing high-performance jet engines. This design aims to enhance broadband stealth capabilities and operational flexibility, positioning the J-36 as a formidable competitor in the realm of sixth-generation fighter aircraft.
Comparing F-47 and J-36

A. Stealth technology and aerodynamics
Building on the F-47’s groundbreaking advancements, a comparison with the J-36 reveals distinct approaches to stealth and aerodynamics. The F-47 features a stealthy nose, bubble canopy, and swept wings for improved control, while the J-36 adopts a triangular, tailless design to reduce radar visibility. Both aircraft aim to surpass current stealth capabilities, with the F-47 potentially offering superior maneuverability due to its more conventional layout compared to the J-36’s unconventional three-engine configuration.
Strategic Implications of Next-Gen Fighters

A. Impact on global air power dynamics
The emergence of sixth-generation fighters like the J-36 and F-47 is reshaping global air power dynamics. These advanced aircraft represent not just military prowess but also strategic ambitions and technological capabilities of their respective nations. The U.S. aims for global dominance with its NGAD program, while China seeks regional influence through the J-36. This competition is likely to influence future military tactics and international relations, potentially escalating tensions in an increasingly polarized world.
| Nation | Aircraft | Strategic Goal |
|---|---|---|
| USA | F-47 | Global dominance |
| China | J-36 | Regional influence |
| Russia | Unnamed | Homeland defense |
B. Influence on future aerial warfare tactics
C. Geopolitical considerations in the Pacific region
Technological Advancements in Both Aircraft

Having compared the F-47 and J-36, let’s delve into their technological advancements. Both aircraft showcase cutting-edge features that redefine aerial warfare:
A. Artificial intelligence integration
- F-47: AI co-pilot for target prioritization and drone coordination
- J-36: Swarm AI for drone control with minimal pilot input
B. Multi-domain operations capabilities
| Aircraft | Capabilities |
|---|---|
| F-47 | Hypersonic missiles (800 km range), directed-energy weapons |
| J-36 | Long-range missiles (3,000 km range) |
C. Enhanced situational awareness and sensor fusion
- F-47: Advanced sensors, superior situational awareness
- J-36: Expected to have advanced radar and sensor systems
Next, we’ll explore the challenges and considerations surrounding these next-generation fighters.
Challenges and Considerations

Development costs and program viability
The transition from strategic implications to practical challenges in next-generation fighter development is marked by significant hurdles. Programmatic uncertainty, stemming from shifting military priorities and political landscapes, complicates development timelines and funding stability. This uncertainty is exemplified by recent pauses in naval NGAD programs. Additionally, industrial limitations and supply chain vulnerabilities, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, threaten timely production and delivery of critical components.

The race between the F-47 and J-36 represents more than just technological advancement in fighter jet capabilities. It symbolizes the ongoing strategic competition between the United States and China in air superiority and military innovation. Both aircraft showcase significant leaps in stealth technology, AI integration, and operational versatility, setting new standards for sixth-generation fighters.
As these advanced jets near operational status, they are poised to reshape aerial warfare and global defense strategies. The F-47’s focus on stealth, agility, and drone collaboration, juxtaposed with the J-36’s emphasis on long-range capabilities and powerful engine configuration, highlights differing approaches to air dominance. Ultimately, the success of these aircraft will depend not only on their technological prowess but also on how effectively they can be integrated into broader military doctrines and adapt to evolving combat scenarios in the coming decade.